Mining professionals often face various challenges when it comes to understanding the material composition of ores. Knowing what’s inside these ores is crucial for effective mineral processing. But how do we go about determining that composition? The research methods for identifying ore composition involve analyzing both chemical and mineral components. Chemical analysis detects the elements that make up the ore, while mineral analysis reveals which minerals are present. This information helps in deciding the most efficient processing strategies to recover valuable resources. A thorough understanding of the material composition of ores greatly impacts mineral processing decisions. This means determining both the useful elements that can be extracted and the potentially harmful components that must be managed during processing. If you want to optimize the recovery of valuable materials, studying these aspects closely is essential.
What Are The Chemical Components of Ores?
Do you know what elements are hiding within your ore? Knowing this is key to profitability. The chemical composition of an ore refers to the various chemical elements present and their relative amounts. This includes both valuable elements and impurities. For example, an iron ore might contain iron, but also silicon, aluminum, and other elements. What are the key chemical indicators we should focus on when analyzing ores? The chemical components of ores can be analyzed through methods such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), and wet chemistry techniques. These methods help identify elements like gold, copper, iron, and lead, crucial for deciding on processing methods.

When we look deeper into chemical analysis, we must consider different techniques. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses. For example, XRF is non-destructive, making it popular for quick and effective analysis. On the other hand, AAS provides highly accurate results but can require more sample preparation. Here is a simple breakdown of the main methods and their characteristics:
| Method | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) | The non-destructive technique that analyzes elemental composition. | Fast analysis, minimal sample prep. | Lower accuracy for light elements. |
| Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) | Measures the concentration of elements in a sample. | High accuracy and sensitivity. | Requires extensive sample prep. |
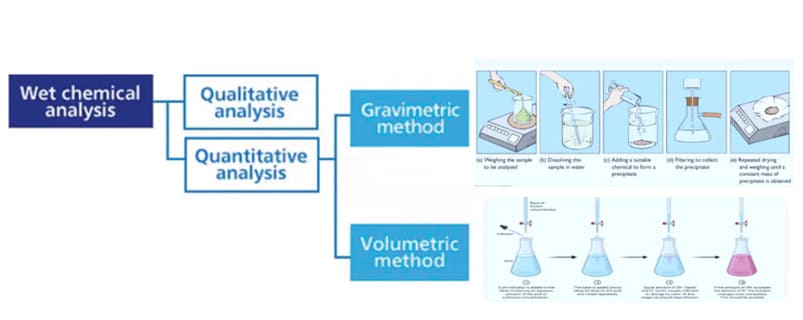
| Wet Chemistry | The traditional method uses chemical reactions. | It can be very accurate. | Time-consuming and labor-intensive. |
If you are in mining, it’s a good idea to become familiar with these methods. They can help you choose the right approach for your ore analysis needs.
How to Detect The Chemical Composition of Ores?
Spectral Analysis
Spectral analysis can quickly and comprehensively identify the types of elements contained in the ore and their approximate content range (qualitative, semi-quantitative), so as not to miss some rare, scattered, and trace elements. Therefore, this method is often used to census the original ore or product. After finding out which elements are contained, a quantitative chemical analysis is carried out. This is very important for considering comprehensive recovery and correctly evaluating the quality of the ore in the beneficiation process.
Chemical Full Analysis And Chemical Multi-element Analysis
Chemical analysis methods can accurately and quantitatively analyze the content of various elements in the ore, and determine which elements must be considered for recovery in the mineral processing process, and which elements are harmful impurities that need to be separated. Chemical analysis is used to understand the content of all material components contained in the ore. For all aspects found through spectral analysis, except for traces, the sum of all other elements as chemical analysis items should be close to 100%. Chemical multi-element analysis is a quantitative chemical analysis of multiple important and more important elements contained in the ore, including not only beneficial and harmful elements, but also slag-forming elements. For example, a single iron ore can be analyzed for total iron, soluble iron, ferrous iron, S, P, Mn, SiO₂, Al₂O₃, CaO, MgO, etc.
What Are The Mineral Compositions of Ores?
Spectral and chemical analyses can only identify the types and amounts of elements contained in the ore. Mineralogical analyses can further identify what kind of minerals exist in the various elements in the ore, as well as the content of various minerals. Once you've established its chemical components, how do we analyze and understand the mineralogical aspect? Mineral compositions of ores can be explored through techniques such as optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Understanding the mineral makeup helps identify the valuable components and can refine extraction processes.
An in-depth examination of mineral composition might also involve a combination of techniques. Optical microscopy, for instance, is often used to get a visual understanding of the minerals present. SEM can reveal microstructural details that are crucial for understanding how the minerals might behave during processing. Let’s break down these techniques further:
| Analysis Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Optical Microscopy | Allows for initial visual characterization. | Quick and cost-effective. | Limited in resolution. |
| Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) | Provides detailed imaging of mineral surfaces. | High resolution for micro-structures. | Requires sample preparation. |
| X-ray Diffraction(XRD) | Identifies minerals based on their crystalline structure. | Comprehensive mineral identification. | More time-consuming. |
Understanding the mineral composition is key to determining effective extraction processes. Certain minerals may dictate the processing methods used.
How to Detect The Mineral Composition of Ores?
Chemical Phase Analysis
The principle of phase analysis is that the solubility and dissolution rate of various minerals in the ore are different in various solvents. Using various solvents of different concentrations to treat the analyzed ore samples under different conditions can separate the various minerals in the ore, so as to measure the presence and content of a certain element in the sample.
Microscope Analysis
Microscope analysis uses the differences in the optical properties of different minerals under the microscope to identify different mineral types and determine the mineral content according to the area occupied by mineral particles in the field of view of the microscope. Commonly used microscopes include solid microscopes (binocular microscopes), polarizing microscopes, and reflective microscopes.
Instrumental Analysis
For the situation where the occurrence state of elements in the ore is relatively complex, in-depth investigation is required, using some special or new methods, such as thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis, electron microscopy, polarography, electrodialysis, laser microspectroscopy, ion probe, electron probe, infrared spectroscopy, etc.
Quantitative Analysis of Mineral Composition
There are many methods for the quantitative determination of minerals in ores. Judging from the current application of various methods, the basic methods of mineral quantification mainly include:
- Separation mineral quantification method: heavy liquid separation, gravity separation, magnetoelectric separation, selective dissolution, etc..
- Microscope quantification method: line measurement method, surface measurement method, point measurement method;
- Characteristic element chemical analysis quantification method: calculate the content of various minerals based on the complete chemical analysis and the content of different characteristic elements of different minerals.
- Instrumental analysis quantification method: X-ray diffraction, IPS, QEM, SEM, MLA, etc.
Conclusion
Understanding the material composition of ores, both chemically and mineralogically, is crucial for efficient mining and mineral processing. Several analytical methods exist, each with its strengths and limitations. Choosing the appropriate method depends on the specific needs and available resources. Combining techniques often provides the most comprehensive picture. Remember, accurate data drives profitable and sustainable mining operations.
